6 Popular Types of Kaydon Bearings and Their Uses
Kaydon Bearings are known for their high quality and versatility, making them a preferred choice across various industries. This blog will explore...

Table of Contents
Bearings are crucial for smooth and efficient motion in mechanical systems, while reducing friction, wear, and noise.
There are various types of bearings, including ball bearings, roller bearings, Slewing Ring Bearings, etc.
This guide will explore different types of bearings, their working principles, advantages and disadvantages, common applications, and best practices for selection and maintenance.

The primary purpose of bearings is to support loads with minimal friction and wear, ensuring efficient motion, reducing energy consumption, and providing stability, precision, and reliability to mechanical systems while minimizing noise and vibration.
Ball bearings use rolling balls to reduce friction and can handle radial or thrust loads.
They have a compact design, require minimal lubrication, and are cost-effective.
However, these types of bearings have limited load capacity, are sensitive to misalignment and contamination, and can be noisy.
They are used in electric motors, automotive wheels, machinery, aerospace, and household appliances.
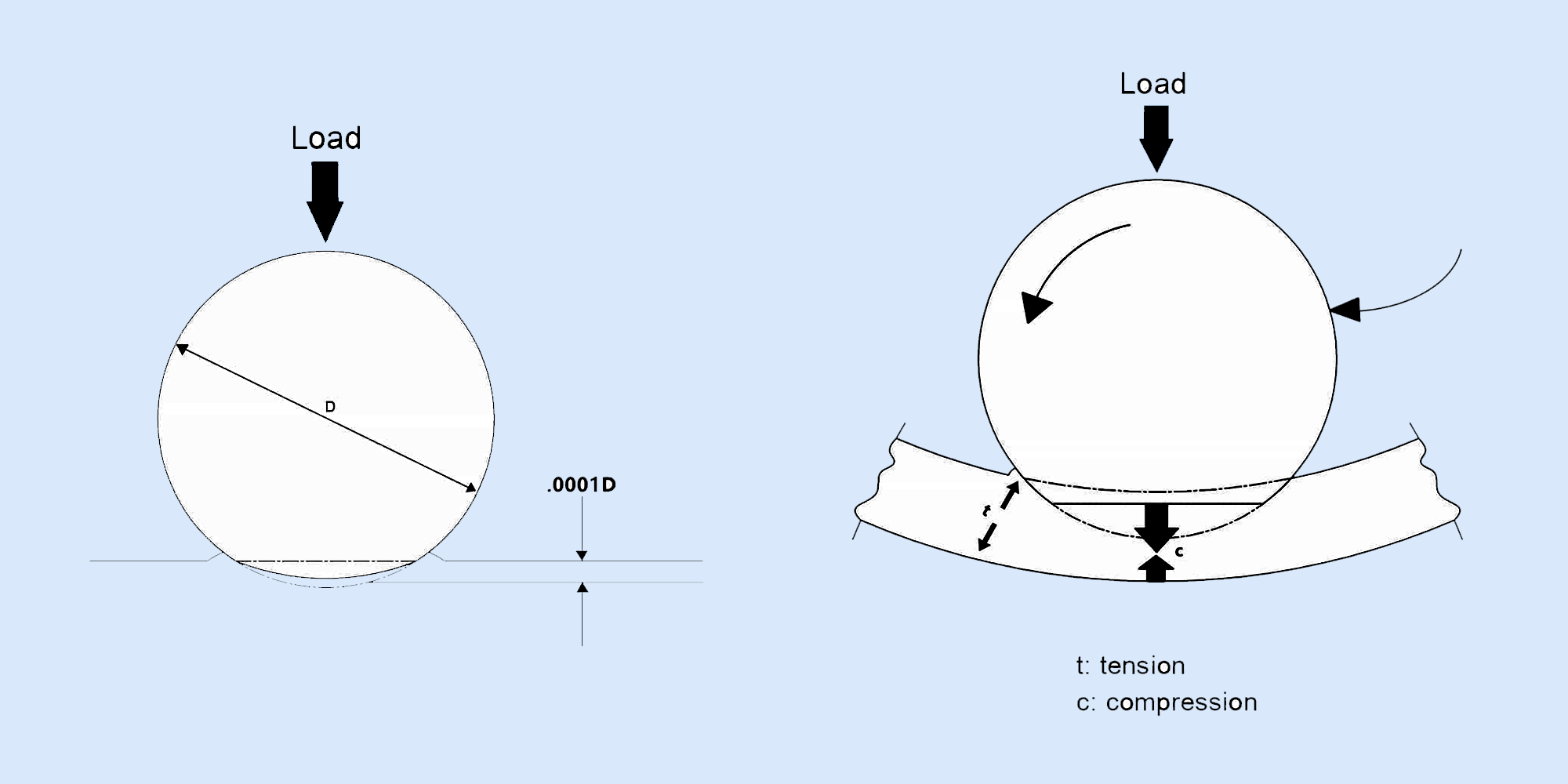
When choosing ball bearings, it's essential to consider factors (see the figure below) such as load capacity, speed and precision requirements, size and fit compatibility, lubrication and sealing needs, tolerance for runout and rigidity, material and construction suitability for the environment, etc.
For more details, please refer to the figure below.

Types of ball bearings:
 Miniature Bearings like the 608 Metric Standard offer high precision and reliability, low noise and vibration levels, reduced weight and friction, and improved energy efficiency.
Miniature Bearings like the 608 Metric Standard offer high precision and reliability, low noise and vibration levels, reduced weight and friction, and improved energy efficiency.
They are ideal for limited space or high-speed applications, and can handle both radial and axial loads.
 Thin Section Bearings offer advantages such as a smaller cross-section, reduced weight, higher precision, lower torque and friction, and high-speed capabilities, making them ideal for space-limited, weight-sensitive, and high-speed applications with improved efficiency and energy consumption.
Thin Section Bearings offer advantages such as a smaller cross-section, reduced weight, higher precision, lower torque and friction, and high-speed capabilities, making them ideal for space-limited, weight-sensitive, and high-speed applications with improved efficiency and energy consumption.
 Flanged Bearings have a flange on the outer ring that simplifies mounting onto a shaft or housing.
Flanged Bearings have a flange on the outer ring that simplifies mounting onto a shaft or housing.
They are suitable for applications with limited space or where a stationary component is required, and they can handle both radial and axial loads.
 Self-aligning Ball Bearings have a continuous spherical outer ring raceway, allowing the inner ring and ball complement to swivel for self-alignment.
Self-aligning Ball Bearings have a continuous spherical outer ring raceway, allowing the inner ring and ball complement to swivel for self-alignment.
They absorb radial forces, making them ideal for applications with shaft and housing misalignment, and feature a double row of balls guided by a cage and inner ring raceway.
 Angular Contact Ball Bearings are ideal for combined loads as their specific contact angle enables the transfer of forces between the two raceways.
Angular Contact Ball Bearings are ideal for combined loads as their specific contact angle enables the transfer of forces between the two raceways.
They are suitable for diverse industrial applications that demand precise and high-performance operation, particularly for transferring high axial and radial forces.
 Deep Groove Ball Bearings are highly versatile, with a capacity for high radial and axial loads, low friction, and high-speed operation.
Deep Groove Ball Bearings are highly versatile, with a capacity for high radial and axial loads, low friction, and high-speed operation.
They have a simple design that makes them easy to maintain and suitable for various applications.
These types of bearings have low torque, making them ideal for high-speed operations.
 Thrust Ball Bearings are types of bearings that handle axial loads in one or both directions with high-speed capabilities.
Thrust Ball Bearings are types of bearings that handle axial loads in one or both directions with high-speed capabilities.
They offer low friction, high precision, and compact design for easy installation and maintenance, often used with other bearings to support rotating machinery.
 Ceramic Ball Bearings are made with ceramic materials like silicon nitride or zirconia, offering superior hardness, reduced friction, and excellent resistance to heat and corrosion compared to traditional steel bearings.
Ceramic Ball Bearings are made with ceramic materials like silicon nitride or zirconia, offering superior hardness, reduced friction, and excellent resistance to heat and corrosion compared to traditional steel bearings.
They are ideal for high-speed applications, extreme temperatures, and environments exposed to corrosive substances.
For more information on ceramic bearings and their applications, visit Ceramic Bearings.
Roller bearings utilize cylindrical, tapered, spherical, or needle-shaped rollers to evenly distribute loads, reducing stress and friction for smooth motion.
Advantages include high load capacity, improved efficiency, rigidity, accuracy, low vibrations, easy maintenance, and axial displacement adjustment.
Disadvantages include higher cost and noise. These types of bearings are used in automotive, industrial, aerospace, construction, energy, railway, marine, etc.
When choosing the right roller bearing, consider factors such as load capacity, speed requirements, operating conditions, mounting and installation, and budget.
Here are some common roller bearing types.
 Tapered roller bearings utilize tapered rollers to handle both radial and axial loads, providing high load capacity and efficient transfer of forces.
Tapered roller bearings utilize tapered rollers to handle both radial and axial loads, providing high load capacity and efficient transfer of forces.
They are widely used in various industries and offer reliable performance and durability.
 Cylindrical roller bearings use cylindrical rollers to provide high radial load capacity and good rigidity.
Cylindrical roller bearings use cylindrical rollers to provide high radial load capacity and good rigidity.
They are widely used in different industries and offer reliable performance, long service life, and low friction.
 Spherical roller bearings feature barrel-shaped rollers arranged in two rows, offering high radial load capacity and the ability to accommodate misalignment.
Spherical roller bearings feature barrel-shaped rollers arranged in two rows, offering high radial load capacity and the ability to accommodate misalignment.
They are utilized in various heavy-duty applications and offer excellent durability and performance.
 Needle roller bearings use thin, cylindrical rollers that are longer than their diameter to provide high radial load capacity in tight spaces.
Needle roller bearings use thin, cylindrical rollers that are longer than their diameter to provide high radial load capacity in tight spaces.
They are widely used in various industries and offer excellent performance, reliability, and space-saving design.
 Spherical roller thrust bearings use asymmetrical barrel-shaped rollers that can handle high axial loads and misalignment.
Spherical roller thrust bearings use asymmetrical barrel-shaped rollers that can handle high axial loads and misalignment.
They are widely utilized in various heavy-duty applications and offer excellent performance, durability, and load-carrying capacity.
 Cross roller bearings utilize cylindrical rollers arranged in a cross pattern to offer high radial and axial load capacity with low friction.
Cross roller bearings utilize cylindrical rollers arranged in a cross pattern to offer high radial and axial load capacity with low friction.
They are widely used in different industries and offer precise motion control, compact design, and reliable performance.
Maintain these types of bearings with proper lubrication, regular inspection, correct handling, avoidance of overload and misalignment, and clean environment.
Slewing ring bearings support heavy loads and ensure efficient load transfer and smooth rotation.
They have advantages like high load-bearing capability, versatility, customizability, space-saving design, and smooth rotation.
However, they come with higher cost, complex installation, heavy weight, misalignment sensitivity, and regular maintenance requirements.
Slewing bearings offer a wide variety of solutions for the most demanding specifications in a variety of applications, including Heavy equipment, Aerospace and defense, Robotics, Renewable energy, Medical systems, etc.
Select slewing ring bearings based on load capacity, stiffness, operating conditions, mounting, gear requirements, and maintenance.
Types of slewing ring bearings include ball slewing bearings, Roller Slewing Ring Bearings, Combination Slewing Ring Bearings, Thrust Ball Slewing Rings, wire race bearing, etc.
Some are standardized and some with flanged. Gears for these slewing bearings include external gears and internal gears and some without any gears.
For more details of these types of bearings and their features, refer to the following picture.

Best practices for maintaining types of slewing ring bearings include regular inspection, proper lubrication, correct handling and installation, avoiding overload and misalignment, keeping the environment clean, and following manufacturer's guidelines.
Cam followers are types of bearings that follow a cam lobe profile to transmit motion and load between machine parts.
Despite offering high load capacity, they have limitations in high-speed or high-precision applications and require more maintenance.
These types of bearing are widely used in machinery, aerospace, food processing, etc. Consider their pros and cons before choosing.
When selecting cam followers, you have to consider factors such as load capacity, operating conditions, cam profile, bearing type, lubrication, mounting and installation, cost-effectiveness, and manufacturer reputation.
Two main types of cam followers:
Refer to the two figures below, you'll have a clearer idea of the above two cam followers.

To well maintain cam followers, you have to inspect for wear/damage, ensure proper mounting and alignment, avoid overloading, monitor operating conditions, follow manufacturer's lubrication recommendations, and choose quality followers from reputable manufacturers.
Plain bearings are types of bearings which minimize wear and friction between two surfaces using low-friction materials and lubrication.
Advantages include simple design, self-lubrication, and heavy load handling.
Disadvantages include higher friction, wear over time, and maintenance requirements.
Used in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and power generation for low-friction sliding or rotational motion.
When choosing plain bearings, you have to consider the load capacity, operating conditions, bearing type, material selection, lubrication, clearance, installation and alignment, etc.
Types of Plain Bearings include:
The two figures below shows the features of the above two plain bearings.


To maintain plain bearings, it is recommended to lubricate them regularly, ensure cleanliness, proper alignment and clearance, control temperature, inspect for wear and damage, replace worn-out bearings promptly, and follow the manufacturer's guidelines.
Linear bearings are types of bearings which enable smooth and precise linear motion using a carriage with a rolling element that moves along a rail or track.
Advantages include high precision, low-friction motion, and long service life.
Disadvantages include higher cost and sensitivity to dirt, debris, and potential noise or vibration.
They are widely used in CNC machines, industrial automation, medical equipment, and printing and packaging machinery.
When choosing linear bearings, consider factors such as load capacity, operating conditions, bearing type, material selection, lubrication, clearance, installation, cost-effectiveness, and manufacturer reputation for reliable and efficient linear motion.
Types of Linear Bearings:
See the figure for a detailed classification of linear bearings.

To maintain linear bearings, you have to do regular lubrication, keeping clean, proper clearance and alignment, monitoring for wear and damage, prompt replacement of worn-out bearings, following manufacturer's recommendations, providing training for personnel, and consulting with experts for specific maintenance requirements, etc.
Mounted bearings are pre-assembled units that reduce friction and wear, supporting rotating shafts in stationary housings.
These types of bearings offer easy installation, versatility, and reduced maintenance, but have higher initial cost, potential for misalignment, and limitations in high-speed or high-precision applications.
They are widely used in various industries such as conveyors, HVAC systems, food processing, packaging, agriculture, mining, construction, etc.
When selecting mounted bearings, consider load capacity, operating conditions, types of bearings, material, lubrication, clearance, tolerances, cost-effectiveness, manufacturer reputation, and ease of mounting.
Types of mounted bearings:
For more details of these types of bearings, please see the figure below.

To maintain mounted bearings, follow best practices such as regular lubrication, proper cleaning, alignment, temperature monitoring, inspection for wear and damage, prompt replacement of worn-out bearings, training personnel, following manufacturer's recommendations, and consulting experts for specific maintenance requirements.
Bearings are vital for supporting motion, heavy loads, and reducing friction, wear, noise, and vibration.
Types of bearings include ball, roller, plain, and linear, each with their own pros and cons.
Choosing the right bearing based on load capacity, speed, environment, temperature, and maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and reliability.
Proper maintenance, including lubrication and wear monitoring, is essential for extending lifespan.
Seek guidance from experts in selecting and maintaining the right types of bearings.

Kaydon Bearings are known for their high quality and versatility, making them a preferred choice across various industries. This blog will explore...
Bearings play a vital role in machinery by ensuring smooth motion and reducing friction. Understanding load capacities, specifically static load vs...

Why Bearing Lubrication is Important Effective bearing lubrication is crucial for the optimal performance and longevity of bearings. It's widely...