Bearing Seal Types & How to Select the Best
Whether you’re working with roller bearings, stainless steel ball bearings, or spherical roller bearings, bearing seals play an essential role in...
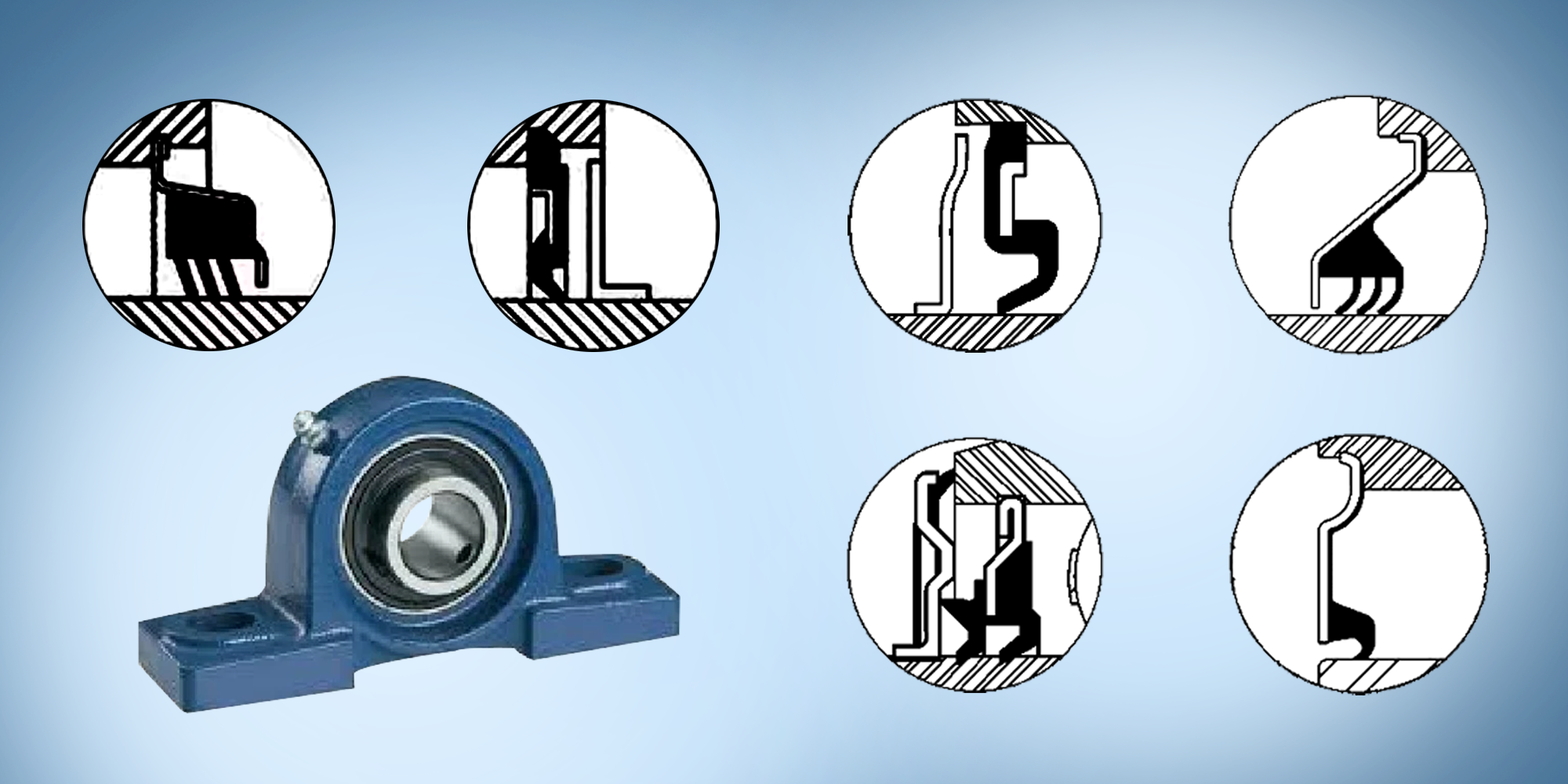
Pillow block bearings are indispensable components in a wide array of industrial equipment, providing robust support for rotating shafts. However, the efficiency of bearings heavily relies on seals.
Seals act as critical barriers. They prevent contamination, retain lubrication, and maintain the operational integrity of the bearing assembly. Bearings seals types vary greatly depending on their intended use.
In this blog post, we'll focus on two main types of pillow block bearing seals --- Lip Seal vs. Labyrinth Seal.
Lip seals are a type of contact seal, specifically engineered for dynamic shaft sealing applications.

Fig 1 Contact Seal
With a notched inner perimeter, these ring-shaped elastomeric components operate by establishing direct frictional contact with the shaft.
This interaction can keep a thin layer of lubricant between the lip and the shaft. This layer is important for making an effective seal.
They generally feature a metal case and an elastomer sealing lip. Many designs also add a garter spring that ensures consistent contact pressure.
Cost-effective, ideal for light-duty applications (such as conveyor idlers).

Fig 2 Single Lip Seal
The primary lip ensures leak prevention, while the secondary lip provides dust protection (e.g., agricultural bearings).

Fig 3 Double Lip Seal
Ideal for extreme contamination scenarios (e.g., in mining machinery).

Fig 4 Triple lip Seal
Lip Seals for pillow block bearings are made of elastomeric materials. They remain reliable even when subjected to significant heat and pressure.
Temperature range:
Temp Range:
Designed only for low to moderate pressure differentials. High pressures can deform the flexible sealing lip, leading to immediate leakage or premature failure.
Lip seals are highly sensitive to shaft condition, which directly impacts their life and effectiveness.
Problems like an improper surface finish, insufficient hardness, excessive runout, or misalignment can compromise the seal.
In some cases, prolonged use can even lead to the seal causing wear or grooving on the shaft itself, especially when lubrication is poor.
Environmental Limitations
Beyond the industry's standard designations like 2RS, some manufacturers also have their own specific seal codes.
See the table below for details.
|
Designation |
Manufacturer |
Description |
|
2RSR |
FAG |
Two standard contact seals. |
|
2RS1 |
SKF |
Two standard contact NBR seals. |
|
2RSL |
SKF |
Two low-friction NBR contact seals. |
|
2BRS |
FAG |
Two low-friction contact seals. |
|
DDU |
NSK |
Two standard contact seals. |
|
DDG |
NSK |
Two high-performance contact seals (enhanced sealing). |
|
DDW |
NSK |
Two high-performance contact seals (enhanced sealing/water resistance). |
|
LLU |
NTN / Enduro Bearings |
Two contact seals (NTN: strong; Enduro: medium). |
|
LLB |
NTN / Enduro Bearings |
Two light-contact seals (NTN); Light contact (Enduro). |
|
LLH |
NTN |
Two low-torque synthetic rubber seals. |
|
LLE |
NTN |
Two water-resistant synthetic rubber seals. |
|
LLU-X |
NTN |
Two enhanced-effect seals. |
|
2RU |
Koyo |
Two standard contact seals. |
|
(RS suffix) |
Timken |
Indicates a rubber seal. |
A labyrinth seal is a type of non-contact seal designed to protect bearings in rotating equipment. It consists of two non-contacting rings that form a complex, winding path.
This seal design effectively restricts the ingress of contaminants such as dirt, splashing liquids, or particulate matter.

Fig 5 Centrifugal Force
|
Seal Type |
Contamination Level |
Material |
Path Pattern |
Key Features |
Installation Method |
|
CF |
Heavy |
Steel / Aluminum |
Most Complex / Winding |
Uses axial capillary & radial centrifugal forces; protects when stationary. Steel versions allow bearing preloading. |
Directly against bearings; uses bearing tolerances. Some versions require axial clamping. |
|
L & M |
Moderate |
Steel / Aluminum |
Sawtooth |
M-series includes outer drain grooves. |
Offset from bearings; uses independent tolerances (press fit). |
|
S & SA |
Moderate (Corrosive) |
High-Perf. Plastic |
Conical Sawtooth |
SA-series includes outer drain grooves. |
Offset from bearings; uses independent tolerances (press fit). |

Fig 6 CF Seal

Fig 7 L Seal

Fig 8 M Seal

Fig 9 S Seal

Fig 10 FA Seal
Choosing the right seal for your pillow block bearing is a critical decision.
Labyrinth seals are ideal for high-speed applications, such as in electric motors and turbines. Their lack of friction provides a major advantage in these environments.
On the other hand, lip seals are a more cost-effective option for general machinery. They offer excellent static sealing and are best for applications with lower speeds and moderate contamination.
|
Feature |
Lip Seal |
Labyrinth Seal |
|
Sealing Principle |
Direct shaft contact |
Non-contact; Centrifugal path |
|
Friction |
High |
Negligible |
|
Speed Limit |
<3,000 rpm |
>10,000 rpm |
|
Temperature Range |
-40°C~250°C (NBR/FKM) |
-200°C~1000°C (Inconel) |
|
Pressure Handling |
Low to moderate (≤0.3 MPa/43 psi) |
Poor (flow restriction only) |
|
Static Sealing |
Effective |
Limited (requires magnetic/PTFE aid) |
|
Contaminant Exclusion |
Good (dust/splash resistance) |
Excellent (airborne particles/splashes) |
|
Lubricant Required |
Yes |
No |
|
Shaft Wear |
Yes |
No |
|
Service Life |
5,000–8,000 hours (medium load) |
>50,000 hours (wear-free) |
|
Maintenance |
Periodic replacement |
Minimal (lifetime solution) |
|
Initial Cost |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Typical Uses |
General machinery |
Turbomachinery, high-speed, harsh environments |
Choosing the right seal is vital for your pillow block bearing's longevity.
By carefully considering the operating environment – including speed, temperature, pressure, and the presence of contaminants – alongside the specific advantages and limitations of both lip seals and labyrinth seals, you can ensure optimal protection.
Contact our technical team today for expert seal solution guidance.
Whether you’re working with roller bearings, stainless steel ball bearings, or spherical roller bearings, bearing seals play an essential role in...

What Is a Water Pump Bearing? A water pump bearing is a specialized component designed to support the impeller shaft of an automotive water pump. It...

SKF's Ongoing Seal Business Restructuring SKF AB, a global leader in bearing and seal production, based in Stockholm, Sweden, is undertaking...