The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Full Complement Bearings
Full complement bearings are often overlooked in the assembly of bearings. Unlike rubber seal, steel seal, open type, and UG bearings that we are...
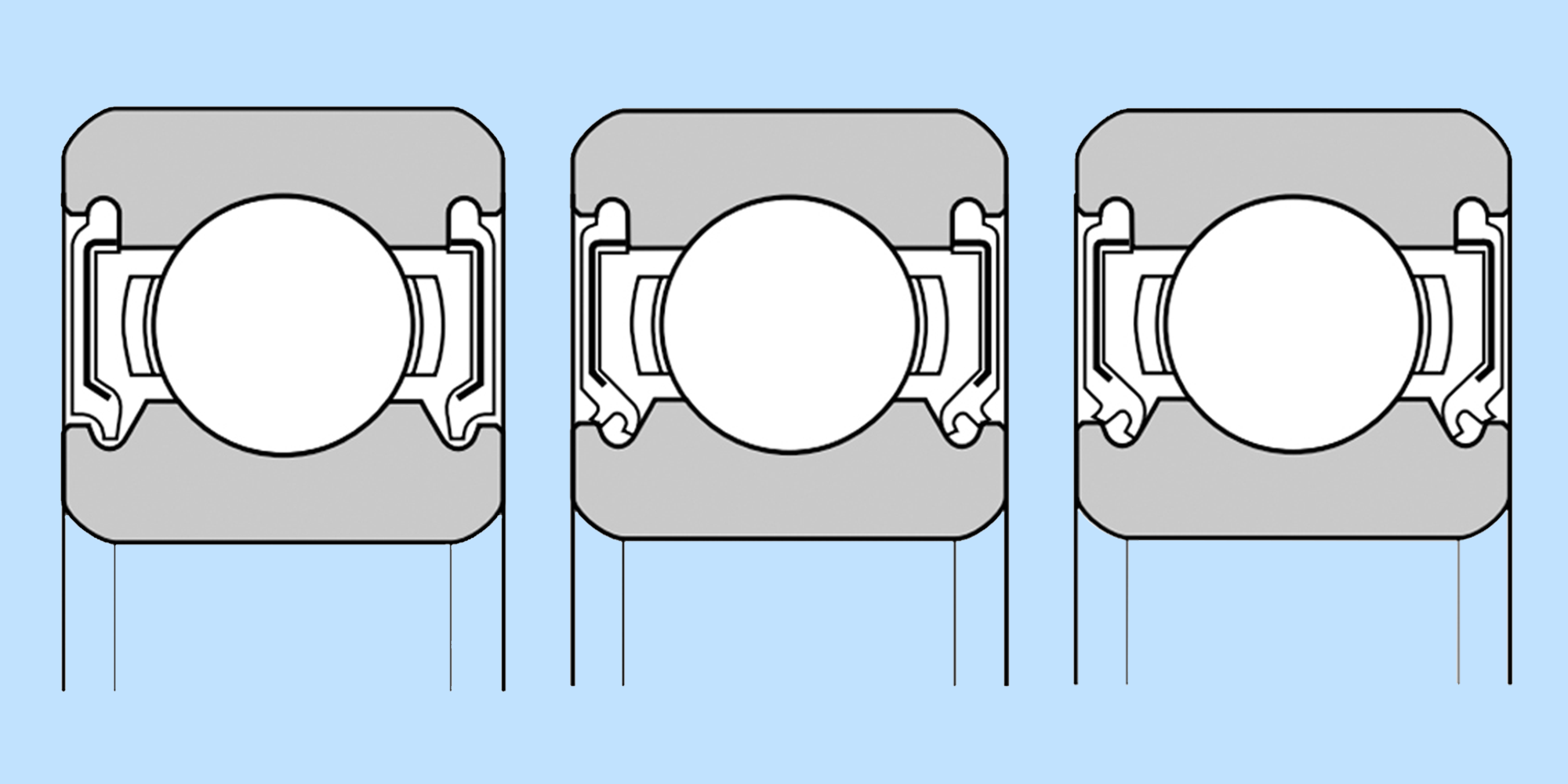
Whether you’re working with roller bearings, stainless steel ball bearings, or spherical roller bearings, bearing seals play an essential role in machinery.
They serve as protective barriers and help extend the bearing's service life, while also promoting smoother and more efficient operation.
This article will dive into the diverse range of bearing seal types to guide your decision-making process.
Bearing seals are components used to protect bearings by keeping out contaminants like dirt, dust, and moisture, while retaining lubricants inside.
This helps extend bearing life and maintain reliable performance.
The right bearing seal is chosen based on several factors, such as operating conditions, speed, and environment, similar to how bearing numbers help identify the correct bearing type.
There are two kinds of bearing seals: contact and non-contact.
While both are essential in machinery, they serve different purposes and are designed for varying types of bearings and applications.
Contact seals are a type of seal where the edge of the seal physically touches the inner raceway of the bearing.
This contact creates a small barrier that helps keep lubricant inside and blocks out dirt, dust and other harmful contaminants.
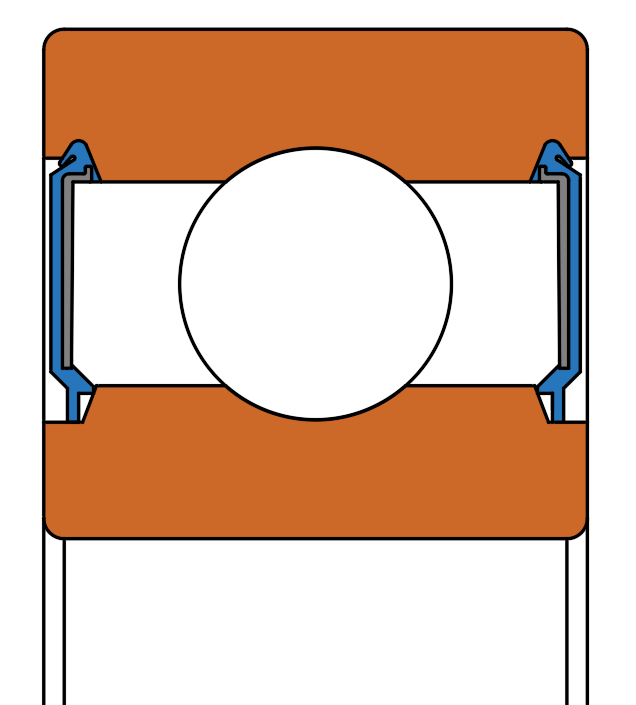
Contact Bearing Seals
Different manufacturers assign unique model series to their contact sealed bearings:
(1) NTN/TPI: LLU,LLH,LLE,LLU-X
(2) NSK: DDG,DDU,DDW
(3) FAG: 2RS, 2RS1
For differences about shields and seals, please see the blog “Shielded Vs Sealed Bearings”.
Non-contact seals operate without physical contact with the corresponding rotating part.
They form a slight gap between the seal and the running surface.
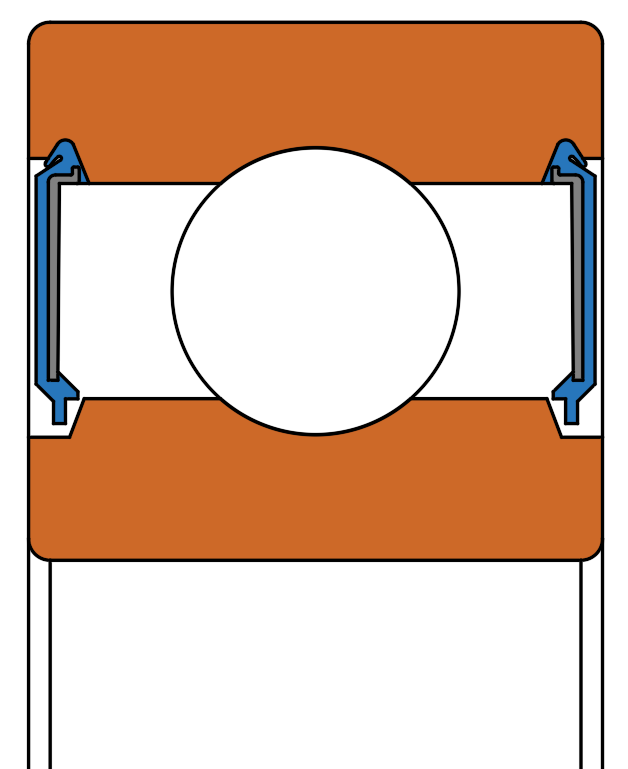
Non-contact bearing seals
Different manufacturers assign unique model series to their non-contact sealed bearings, such as:
The table below illustrates common materials of bearing seal types, their temperature tolerances, and key characteristics:
|
Materials |
Temperature range |
Main Features |
|
Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
-40°C to 110°C |
|
|
Acrylonitrile-Butadiene Rubber (NBR/Buna-N) |
-40°C to 100°C |
|
|
Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM/Viton) |
-40°C to 230°C |
|
|
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
-190°C to 250°C |
|
|
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) |
-70°C to 250°C |
|
While this table provides a general overview, selecting the right material becomes even more critical for specialized hardware.
For a deeper dive into how these materials perform under extreme chemical exposure or high-pressure washdowns, read our specialized guide on sealing and lubrication solutions for stainless steel bearings in harsh environments.
To select the right bearing seal, particularly when developing custom bearings, you have to consider the following factors:
Even the best ball bearing seals require upkeep to sustain maximal bearing life and high performance.
Proper maintenance and timely replacement help to make sure the seals continue protecting against contaminants and retaining lubrication, which helps preserve the health of the bearing and surrounding components.
Understanding and selection of appropriate bearing seal types are crucial for maximizing machinery performance and lifespan.
This choice should consider factors like the bearing application, operating environment, potential contaminants, and lubrication needs.
Keep in mind, consistent maintenance and timely replacement of these seals are key to sustaining their benefits.
The efficiency of your machinery significantly hinges on the informed selection and handling of bearing seals.

Full complement bearings are often overlooked in the assembly of bearings. Unlike rubber seal, steel seal, open type, and UG bearings that we are...
In the realm of industrial machinery, the pursuit of efficiency and longevity is constant. Magnetic bearings emerge as a cutting-edge alternative to...

A spherical roller bearing is a type of bearing that helps support rotating shafts in machines. It has a set of round rollers inside that are shaped...