Double-Direction Thrust Ball Bearings Promoted Water Pumps to Run Well
When you turn on the tap, have you ever wondered how the tap water you use every day reaches the water pipes in your home? Actually, this should be...
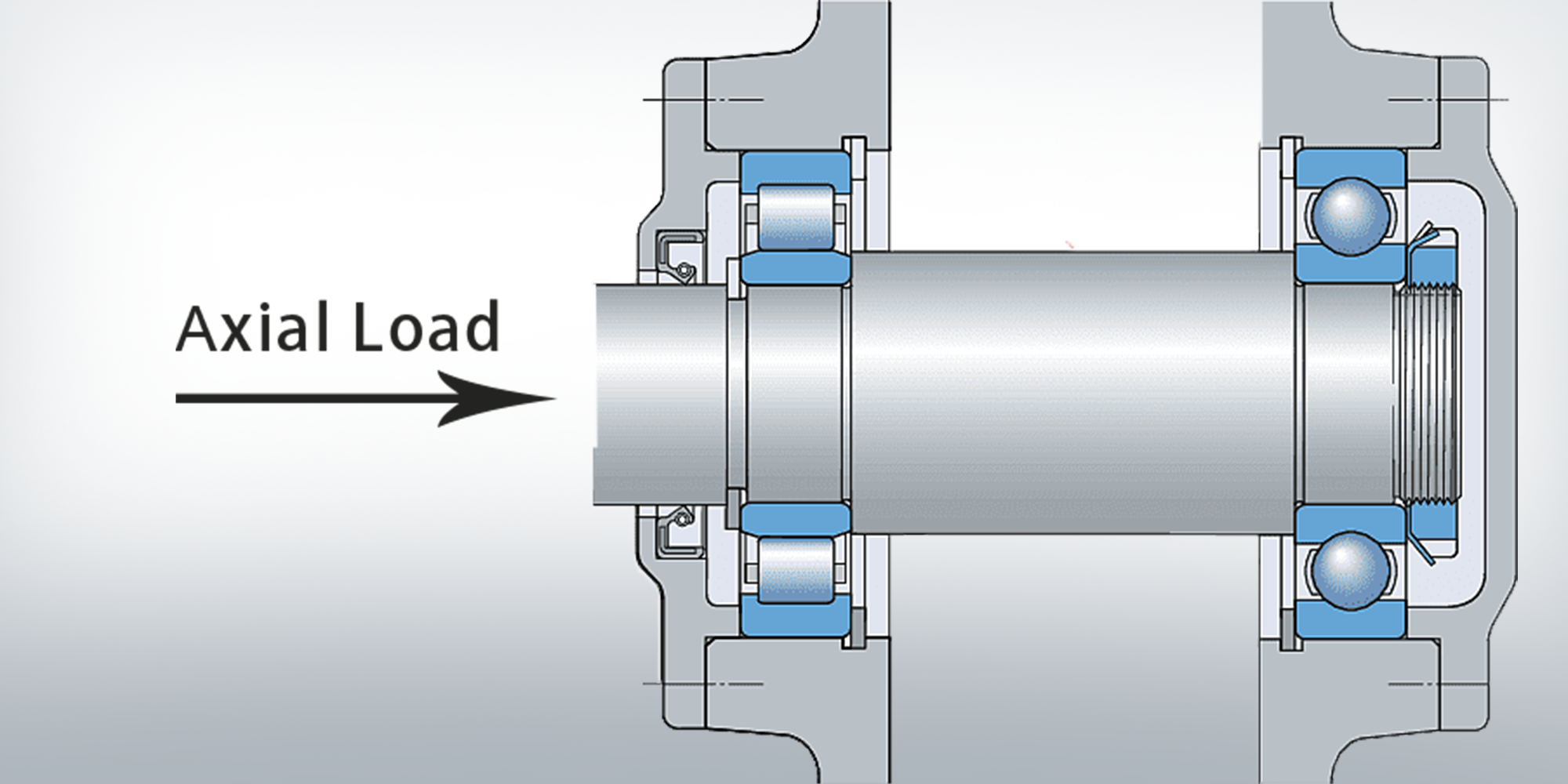
Understanding bearing axial load, just like understanding different types of bearing load, is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning and longevity of mechanical systems that utilize bearings.
This article delves into the intricacies of bearing axial load, its impact on system performance, and best practices for its management.
Bearing axial load is a force applied parallel to the axis of a bearing or mechanical component.
It plays a crucial role in the overall operation of the system in which the bearing is used, directly affecting its performance and efficiency.
The direction of the axial load determines how the bearing distributes this force, and hence, the subsequent reaction within the system.
Whether the axial load is directed towards the center or away from it, it will significantly influence the bearing's reaction and potentially its wear pattern.
Mismanagement of these loads can lead to a range of adverse effects, including accelerated wear, decreased efficiency, and even system failure.
Therefore, comprehending axial load and its correct handling is critical for bearing applications.

External factors greatly impact a bearing's axial load, including:
Internal factors that influence a bearing's axial load capacity include:
Calculating and determining axial load in a bearing involves a series of careful steps that ensure accurate results.
Here is a step-by-step guide:
If the axial load is generated by a known force acting in the direction parallel to the bearing axis, the axial load will be equal to that force.
If the force is not parallel to the bearing axis, the axial load is usually the component of the force vector that lies along the axis of the bearing.
This can be calculated using trigonometry if the angle between the force vector and the bearing axis is known.
In more complex systems, particularly those involving multiple bearings and/or forces in different directions, the axial load on each bearing is typically calculated using principles of statics and dynamics, which involve setting up and solving systems of equations based on force and moment balance conditions.
In many practical cases, engineers use software tools, such as finite element analysis (FEA) programs, to calculate the axial load on a bearing, especially in complex systems where multiple forces, moments, and deformations have to be taken into account simultaneously, like those found in wind turbines or industrial machinery.
Effectively managing and controlling bearing axial load involves several crucial steps:
The repercussions of excessive or insufficient axial loads can severely undermine a bearing's performance.
Overloading can lead to fatigue, premature failure, increased friction, and excessive heat.
Conversely, underloading can compromise the bearing's performance and load-carrying capacity, causing instability and excessive axial movement.

Bearing Failure Due to Overloading
Implementing regular monitoring and maintenance of bearing systems is a key practice for managing axial loads.
Adherence to manufacturer guidelines concerning load ratings and limits is vital.
Furthermore, environmental factors that can affect axial load, such as temperature variations, contaminants and lubrication conditions, should be taken into account.
Understanding and effectively managing bearing axial loads is critical to ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of bearing applications.
At LILY Bearing, we are committed to providing in-depth knowledge, high-quality products, and top-tier customer service to help our clients navigate this important aspect of bearing management.
Our dedication to excellence ensures that with us, your bearings are always in good hands.

When you turn on the tap, have you ever wondered how the tap water you use every day reaches the water pipes in your home? Actually, this should be...
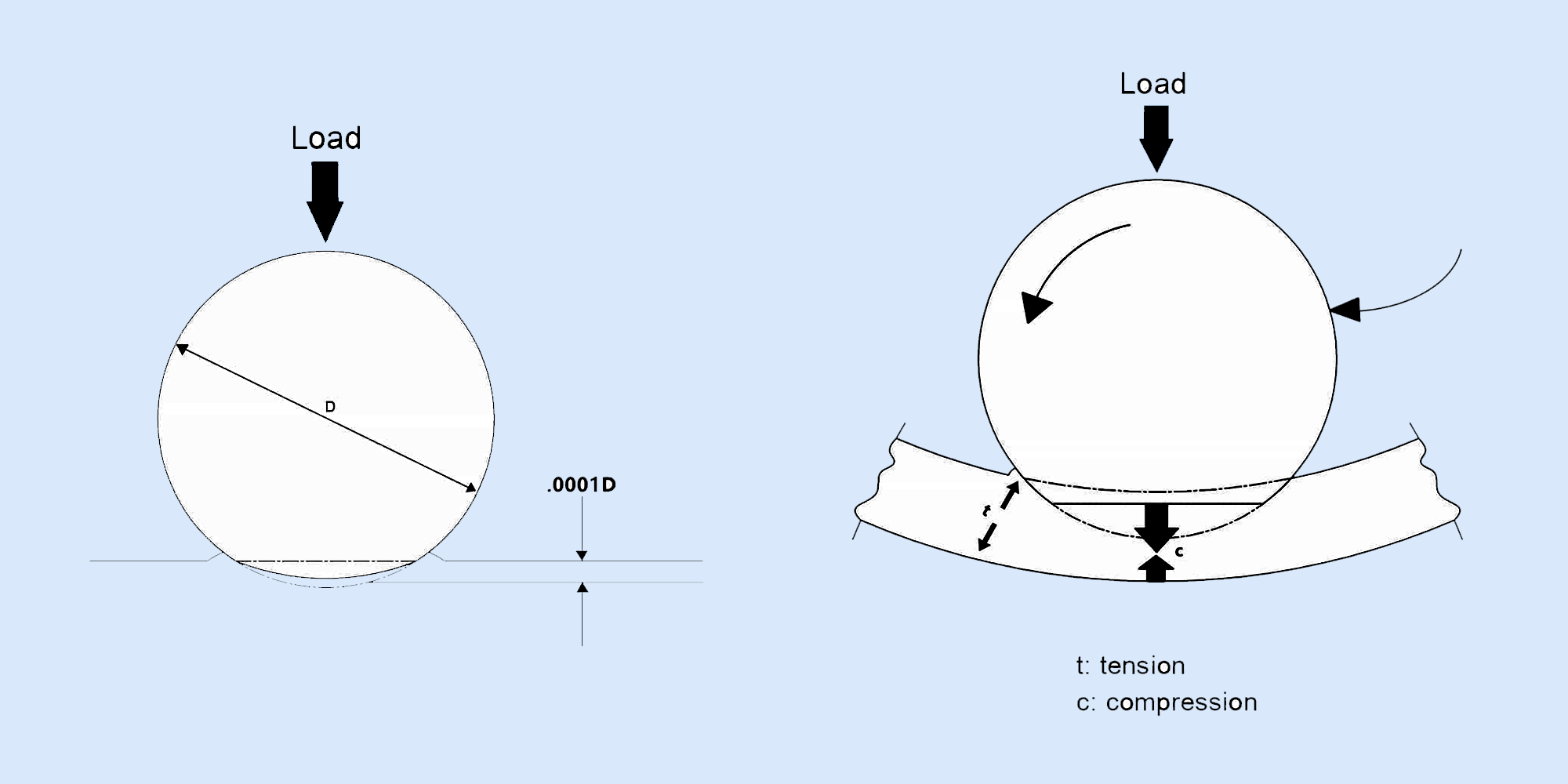
Bearings play a vital role in machinery by ensuring smooth motion and reducing friction. Understanding load capacities, specifically static load vs...

In the vast world of machinery, ever pondered the question, "how do bearings work?" These unassuming devices play a monumental role in numerous...