Maintenance Tips for Cam Follower Bearings
Understanding Cam Follower Bearings What Are Cam Follower Bearings? Cam followers, or cam follower bearings, come with a cage for holding the...

Flanged bearings are essential in industrial machinery. They ensure proper alignment, prevent movement, and provide stability for shafts. This reduces vibration and improves performance. It also contributes to extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Flanged bearings play a key role in machinery by reducing wear on components. They also boost overall efficiency and extend the lifespan of rotating equipment. Their design ensures smooth operation and long-term reliability. This makes them essential for industrial applications.
This blog explains flanged bearings, including their types, features, and benefits. It also covers where they are used and how to maintain them for better performance and longer life.
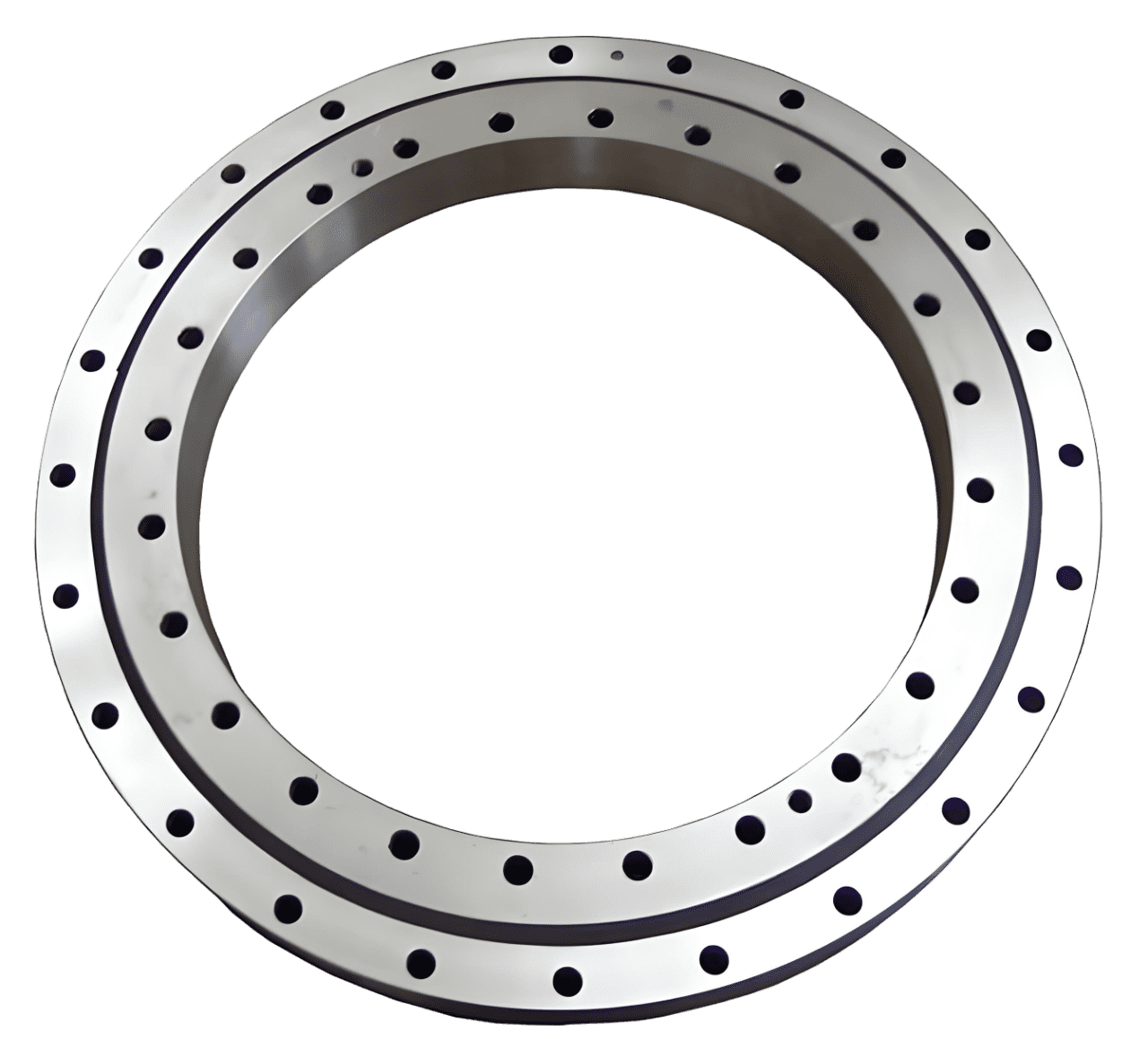
Flanged bearings are bearings with an extended rim, or flange, at one end. This flange simplifies mounting and ensures proper positioning within a housing or tube. It helps maintain stability and alignment during operation.
Flanged bearings are used in machines where precision and stability are important. The flange keeps the bearing in place and helps align the shaft properly. This makes them perfect for equipment like conveyors, robots, and car parts, ensuring smooth and reliable operation.
Open ball bearings have a simple design with an inner race, an outer race, and ball elements. These components work together to allow smooth rolling. They are "open" because they lack seals or shields, which makes them easy to maintain and clean.
Open ball bearings are used in machines with low to moderate speeds. They work well in clean environments where lubrication is easy to apply. They are commonly found in household appliances, electric motors, and bicycles. These applications require simple maintenance and low cost.
Shielded ball bearings have a metal shield on one or both sides of the bearing. The shield acts as a barrier, preventing harmful particles from entering and damaging the internal components.
Shielded ball bearings are used in places where cleanliness matters, but rubber seals aren't needed. They are commonly found in electric motors, fans, and industrial machinery. Keeping dirt and debris out is important for ensuring smooth and reliable performance.
Sealed ball bearings have rubber or metal seals on both sides to fully protect the bearing from dirt, dust, and moisture. These seals keep contaminants out while also keeping the lubrication inside, ensuring smooth operation. This design makes sealed bearings ideal for harsh environments where cleanliness is crucial and long-lasting lubrication is needed. They're commonly used in machinery, automotive parts, and equipment exposed to challenging conditions.
Stainless steel flanged ball bearings are popular because they are durable and resistant to rust. This makes them ideal for tough environments like food processing, marine, and medical equipment. In these environments, moisture and chemicals are common. Their flanged design also makes them easy to install and stable, adding to their reliability in demanding situations.
Two-bolt flanged ball bearings are commonly utilized in machines that handle light loads. They have a flange with two bolt holes that make it easy to mount and keep the bearing stable. These bearings work well in machines where the force is mostly sideways, not along the shaft. They are commonly used in things like conveyor systems, small motors, and light-duty equipment.
Four-bolt mounted bearings are designed for heavy-duty applications, offering several advantages:
Three-bolt flange mounted ball bearings are versatile and work well in machines where a three-point attachment is needed for better support. This design aids in alignment and stability. This makes them particularly suitable for light to medium-duty machines. They are easy to install and provide balanced support.
Flanged wheel bearings are used in wheels and axles to provide stable support, especially in cars and heavy transport systems. The flange keeps the bearing securely in place, allowing the wheel to rotate smoothly.
In cars, these bearings help the wheels move efficiently while supporting the vehicle’s weight. In heavy transport systems like trucks and construction machines, flanged wheel bearings handle high loads, reduce friction, and improve performance.
They are perfect for keeping wheels aligned and stable, whether for everyday vehicles or heavy machinery.
Full complement ball bearings are used when high load capacity and durability are required. They are especially useful in tight spaces where cages cannot be used. These bearings fill all the gaps between the balls with ball elements, so there is no need for a cage to hold them in place.
|
Type of Flanged Bearing |
Material |
Key Features |
Common Applications |
|
Low-Profile Flanged Bearings |
Steel, Cast Iron |
Compact size, space-efficient |
Small machines, compact equipment |
|
Corrosion-Resistant Flanged Bearings |
Stainless Steel, Ceramic |
Resistant to moisture, chemicals, and salt, durable in harsh conditions |
Food processing, marine, medical equipment |
|
Standard Flanged Bearings |
Steel, Cast Iron |
Strong support, reliable for general use |
Industrial machinery, general equipment |
|
Polymer Flanged Bearings |
Plastic (e.g., POM, Nylon) |
Low friction, self-lubricating, wear-resistant |
Light-duty applications, noise-sensitive machines |
|
High-Speed Flanged Bearings |
Ceramic, High-Performance Alloys |
Precision materials, low friction, high efficiency |
High-speed machinery, precision equipment |
|
Type of Flanged Bearing |
Load Capacity |
Speed Ratings |
Applications |
|
Standard Flanged Bearings |
Moderate, suitable for general loads |
Low to moderate speeds |
Industrial machinery, conveyors, general use |
|
High-Performance Flanged Bearings |
High, handles heavy-duty loads |
Optimized for high speeds |
High-speed machinery, precision equipment |
|
Polymer Flanged Bearings |
Low to moderate, ideal for light-duty loads |
Moderate speeds |
Noise-sensitive or lightweight applications |
|
Corrosion-Resistant Bearings |
Moderate to high, depends on material |
Moderate speeds |
Marine, food processing, and harsh environments |
|
Low-Profile Flanged Bearings |
Moderate, compact but sturdy |
Low to moderate speeds |
Small machines, space-constrained setups |
Made from materials like steel or cast iron, these bearings are designed for steady, moderate loads.
Typically used in applications where speed requirements are not excessive, such as conveyors and general machinery.
Constructed from precision materials like ceramic or advanced alloys, these models handle higher loads while reducing wear and tear.
They are ideal for high-speed machinery, offering superior efficiency and longevity even under intense operating conditions.
|
Seal Type |
Design |
Role |
Applications |
|
Open |
No seal or cover; balls are fully exposed |
- Allows easy lubrication. |
Clean environments where regular maintenance is possible, like household appliances or low-speed machinery. |
|
Shielded |
Metal shields on one or both sides |
- Protects against dirt and debris. |
Electric motors, fans, and light industrial machines where some protection is needed. |
|
Sealed |
Rubber or synthetic seals on one or both sides |
- Fully seals the bearing to keep contaminants out and retain lubrication. |
Harsh environments, outdoor equipment, or applications where maintenance is difficult, like pumps and automotive systems. |
|
Material |
Temperature Resistance |
Corrosion Resistance |
Applications |
|
Withstands moderate to high temperatures (up to 300°C depending on grade). |
High resistance to moisture, chemicals, and oxidation. |
Ideal for food processing, marine environments, and moderate heat applications. |
|
|
Handles extreme temperatures (up to 1000°C in some cases). |
Exceptional resistance to corrosion and chemical exposure. |
Perfect for high-speed, high-temperature, or highly corrosive environments, such as aerospace and medical devices. |
|
|
Plastic/Polymer |
Limited temperature resistance (typically below 150°C). |
Resistant to moisture and some chemicals but less durable in harsh environments. |
Used in light-duty applications, such as conveyors or office equipment. |
|
Specialized Coated Bearings |
Enhanced resistance with coatings like Teflon or nickel plating. |
Improved protection against harsh chemicals and extreme moisture. |
Used in applications requiring additional durability, like chemical processing or outdoor equipment. |
Support high loads and endure harsh operating conditions.
Minimize wear and vibration to enhance machinery lifespan.
Mining equipment, industrial presses, and construction machines.
Ensure smooth rotation in critical components like wheels and axles.
Handle high-speed and high-load conditions for efficient performance.
Wheel hubs, drive shafts, and steering systems.
Provide precise alignment for accurate and controlled motion.
Reduce friction for smooth, energy-efficient operation.
Robotic arms, conveyor systems, and automated assembly machines.
Food-grade bearings are designed with materials and lubricants that comply with food safety standards, preventing contamination.
Corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or polymer, withstand regular washdowns and exposure to cleaning agents.
These bearings resist moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations, ensuring reliable performance in challenging conditions like cold storage or high-temperature processing.
Their robust design minimizes wear and tear, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacements. This helps maintain continuous production.
Commonly used in conveyors, mixers, packaging machines, and other equipment in food processing plants.
Precision flanged bearings ensure exact alignment and smooth motion. This is critical for applications requiring high tolerances, such as aerospace navigation systems and medical devices.
These bearings are built to perform in extreme conditions. They offer long-lasting durability and consistent performance, even in high-stress environments like aircraft engines or turbines.
Precision bearings can handle high rotational speeds with minimal friction, improving efficiency and reducing energy loss in critical machinery.
They are widely used in aerospace systems, robotics, optical equipment, and high-speed CNC machines. In these applications, precision and reliability are non-negotiable.
The flange on flanged bearings makes installation easier by providing a built-in guide for proper positioning. This eliminates the need for extra alignment components. The flange keeps the bearing securely in place during setup.
As a result, the installation process is faster, reducing setup time. This makes it more efficient, especially in complex machinery or tight spaces.
Self-aligning flanged bearings can adjust to small misalignments between the shaft and housing. This helps them run smoothly even if there are slight alignment issues. By handling these small misalignments, the bearings reduce wear and prevent early failure. This helps them last longer and keeps the machinery working reliably.
Flanged bearings can handle heavy radial and axial loads, making them perfect for tough environments. The flange helps spread the load evenly, providing stability and reducing stress. This makes them reliable for heavy-duty equipment like construction machines and vehicles.
Applications: These bearings are utilized in wheels, axles, and drive shafts.
Benefits: Ensure smooth motion and high reliability in automotive components, even under high loads.
Applications: Used in food-grade and corrosion-resistant versions for conveyors, mixers, and packaging machines.
Benefits: Maintain hygiene standards, withstand washdowns, and handle exposure to cleaning agents.
Applications: Used in conveyor systems, presses, and heavy-duty machinery.
Benefits: Provide stability, support, and durability in demanding applications.
Applications: Used in robotic arms and automated production systems.
Benefits: Offer precise alignment, smooth motion, and reduced friction for efficient operations.
Flanged bearings are built to last with strong materials like stainless steel or ceramic, which resist wear and corrosion. To help them last even longer, regular maintenance is important. This includes cleaning, adding lubrication, and checking for wear.
Proper lubrication reduces friction, and cleaning removes dirt that can cause damage. Regular checks can spot problems early, helping to avoid bigger issues. This ensures the bearing works smoothly for a long time.
|
Feature |
Flanged Bearings |
|
|
Mounting |
Built-in flange simplifies installation and reduces setup time. |
Requires additional support or mounting components, complicating installation. |
|
Alignment |
Flange helps maintain alignment and tolerates slight misalignments. |
Sensitive to misalignment, requiring precise alignment during installation. |
|
Installation |
Quicker and easier setup because of flange design. |
More time-consuming installation because of the need for accurate alignment. |
|
Forgiveness |
More tolerant of slight misalignments. |
Misalignment can cause uneven wear and failure. |
|
Feature |
Flanged Ball Bearings |
|
|
Ease of Installation |
The flange makes installation easier by providing a built-in guide for alignment, reducing setup time. |
Requires external components or mounting brackets for alignment, making installation more complex. |
|
Alignment |
Flanged bearings maintain alignment better because of the flange, which holds the bearing in place. |
Standard bearings are more prone to misalignment and require more precise setup. |
|
Protection |
Flanged bearings offer additional protection against dirt and debris by keeping the bearing more securely in place. |
Standard bearings may need extra components like seals or shields for protection against contaminants. |
|
Versatility |
Ideal for applications where the bearing needs to stay in place and be easily mounted. |
Suitable for general applications but requires more effort to ensure proper alignment and protection. |
Compact flanged bearings, like low-profile versions, are perfect for tight spaces. They are smaller but still offer the same benefits as larger bearings. These include easy installation, better alignment, and protection from dirt.
Their small size makes them ideal for use in small motors, robots, and other equipment with limited space. They still ensure reliable performance despite their compact design.
Selecting the right flanged bearing is essential for ensuring smooth operation and long-lasting performance.
Do you require assistance in selecting the appropriate flanged bearing? Contact LILY Bearing for detailed specs and expert advice. Our team is here to help you find the best solution for your needs.

Understanding Cam Follower Bearings What Are Cam Follower Bearings? Cam followers, or cam follower bearings, come with a cage for holding the...

Slewing bearings are essential mechanical components that manage axial, radial, and moment loads. They play a critical role in industries such as...
Mounted bearings are essential for industrial machines. They support and stabilize rotating shafts, ensuring they stay aligned and reduce friction....